Volume 3, Issue 1
Author(s): Pritesh Ranjan Dash, Mahmuda Nasrin, Mohammad Shawkat Ali
Abstract: Kaempferia galanga (Family: Zingiberaceae) has been used for the treatment of various skin disorders and widely used in the treatment of nematocide, larvicide, colera and various inflammatory disorders. The study was aimed to investigate the cytotoxic and antibacterial activity of different extracts of the rhizome and leaf of Kaempferia galanga. Cytotoxicity was determined against (Artemia salina) brine shrimp nauplii. The antibacterial activity was performed by disc diffusion method and determination of zone of inhibition of living microorganisms. In the brine shrimp lethality bioassay all the extracts showed moderate cytotoxic activity when compared with the standard drug vincristine sulphate. For example, LC50 value of the acetonic leaf extract was 4.78 μg/ml while the LC50 of vincristine sulphate was 0.52 μg/ml. All the natural products (400 μg/disc) showed moderate antibacterial activity against both gram positive and gram negative bacteria as compared with the standard drug ciprofloxacin (5 μg/disc).
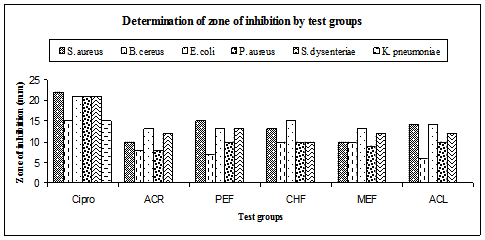
Fig: Antibacterial activity by Kaempferia galanga. Klebsiella pneumoniae was not inhibited by any of the extracts. ACR =Acetone extract of rhizome, PEF= Petroether fraction of rhizome, CHF=Chloroform fraction of rhizome MEF=Methanol fraction of rhizome and ACL=Acetone extract of leaf, Cipro = Ciprofloxacin.
Download Full Article : Click Here
