- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 5 (2025)
Phytochemical profiling and multifunctional bioactivity of Solanum nigrum against multidrug-resistant bacteria
Priyanka Dalwadi, Jasmine A Mansuri, Anjali Thakkar and Anju Kunjadiya
A significant global health concern is the increasing occurrence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial pathogens, which calls for the investigation of new natural antimicrobial agents. The current investigation compared the antibacterial activity of methanolic extracts from Mesua ferrea, Zingiber officinale, Solanum nigrum, and Pueraria tuberosa against MDR bacterial isolates recovered from bovine mastitis milk, including Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus paraanthracis, Alcaligenes faecalis, and Bacillus licheniformis. S. nigrum showed the strongest antibacterial activity among the tested extracts, and it was then thoroughly characterized in terms of phytochemistry and bioactivity. Alkaloids, flavonoids, phenolics, tannins, saponins, and terpenoids were confirmed by qualitative phytochemical screening, thin-layer chromatography (TLC), high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC), and gas chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry (GC-HRMS). One of the main bioactive components was 1-propanol, 2-(1-methyl ethoxy)- [2-2-isopropoxypropane]. Strong free radical scavenging ability (IC₅₀: DPPH 42.6 µg/mL; superoxide 49.2 µg/mL) and catalase inhibition (IC₅₀ 56.1 µg/mL) were shown by antioxidant assays. Protein denaturation was significantly inhibited (78.4% at 100 µg/mL) and red blood cell membrane stabilization was comparable to diclofenac sodium, demonstrating the extract's concentration-dependent anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, MCF-7 breast cancer cells were cytotoxically affected by S. nigrum extract (IC₅₀ 78.5 µg/mL), exhibiting morphological characteristics that were consistent with apoptosis. Together with strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties, S. nigrum's broad-spectrum antibacterial efficacy points to a variety of therapeutic possibilities. Its various phytoconstituents acting on various cellular targets most likely interact synergistically to produce these effects. The results taken together show that S. nigrum is a promising candidate for the development of plant-based antimicrobial and adjunct therapeutic agents against MDR pathogens, which calls for additional in vivo validation and the isolation of bioactive secondary metabolites by different bioassays.
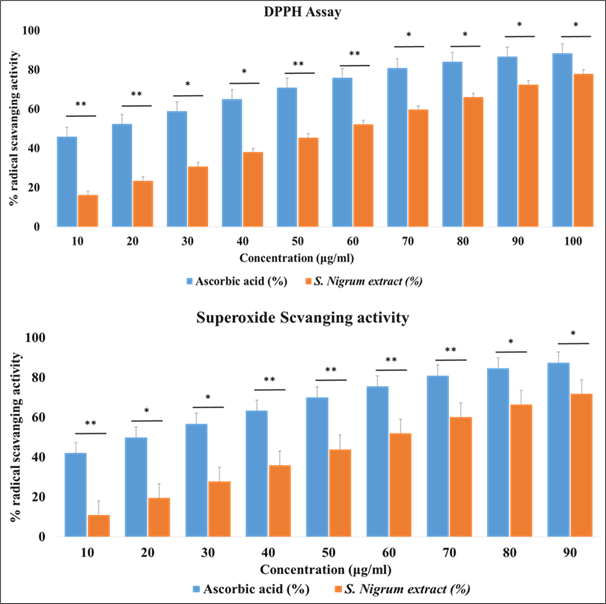
Fig. 1: Dose-response curves of S. nigrum extract in antioxidant assays, A. DPPH, and B. Superoxide scavenging.
Pages: 614-623 | 263 Views 112 Downloads









