- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 5 (2025)
Phytochemical and pharmacological study of medicinally important plant Artemisia pallens wall
Ashwini Mulay, Yogesh Gahile, Tukaram Nikam and Digamber Ahire
Artemisia pallens is a medicinally important plant traditionally used for its antimicrobial, antidiabetic and and antioxidant properties. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the phytochemical profile and pharmacological potentials of whole plant biomass of Artemisia pallens with a focus on solvent-dependant variations.
Plant material was extracted using solvents of varying polarity (distilled water, ethanol, methanol, petroleum ether and chloroform). Quantitative estimation of phenols, flavonoid, tannins and artemisinin was carried out using standard colorimetric methods using spectrophotometer. Pharmacological evaluation included antioxidant evaluated through DPPH radical scavenging assay and hydroxyl radical scavenging assay, while antimicrobial assay was performed against different bacterial strains.
Phytochemical analysis revealed that the presence of phenols was significantly higher in distilled water extract and flavonoids and tannin content were significantly higher in methanolic extracts. Artemisinin content was significantly high in ethanolic extract (1.01 ± 0.04 mg/gm dry biomass). A strong positive correlation was observed between phenolic, flavonoid and tannin levels with both artemisinin content and antioxidant activity.
The study highlights A. pallens as a rich source of bioactive phytoconstituents with strong antioxidant potential. Solvent selection significantly influences phytochemical yield and pharmacological activity, suggesting that optimization of extraction methods can enhance therapeutic efficacy.
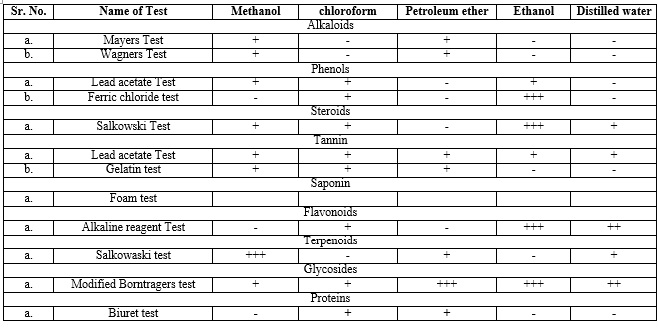
Fig. 1: Qualitative phytochemical analysis of Artemisia pallens Wall.
Pages: 08-15 | 1188 Views 73 Downloads







