- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 5 (2025)
Assessing the effectiveness of Zn-EDTA and Fe-EDTA in agronomic biofortification of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) in alluvial soils of the subtropical region of Uttarakhand
Himanshu Negi, Thounaojam Babina and Huidrom Shilpa
Micronutrient deficiencies also renowned as “Hidden hunger” is a concerning health issue in modern day scenerio. Trace elements like Zinc and Iron are required for normal biochemical and physiological bodily functions of a person. Meager intake of these minerals due to a nutrient deficient diet, triggers various diseases and disorders. Agronomic biofortification is a strategic augmentation of the nutritional profile of primary food crops by using fertilizers. A field experiment was conducted during the rabi season of 2024-25, at Agronomy Research Field of Department of Agronomy, DIBNS Manduwala, Dehradun with the aim of identifying the effectiveness of zinc and iron chelate (EDTA) fertilizers in agronomic biofortification of barley (variety RD 2552). The study was carried out in randomized block design with seven treatments and three replications. The results of the study revealed that T7 (RDF + Zn-EDTA @ 0.75% + Fe-EDTA @ 0.75%) significantly increased the grain zinc (62.41 mg/kg), iron (80.05 mg/kg) and protein content (19.59%) also T7 maximized the biological performance of crop in terms of growth attributes viz plant height, tillers number per plant, dry weight/plant, which collectively translated into maximum yield and associated traits.
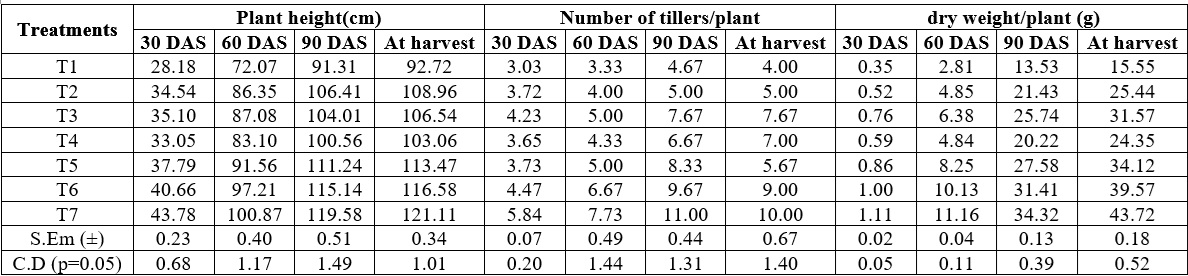
Fig. 1: Effect of Zn EDTA and Fe EDTA application on growth attributes of barley
Pages: 31-34 | 1786 Views 59 Downloads







