- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Peer Reviewed Journal
Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 5 (2025)
Advances in semi-synthetic derivatives of quercetin: Enhanced methodologies and pharmacological potential
Author(s):
Chaitra S Shriyan, Iravati J Chengalur and Vishal Banewar
Abstract:
Quercetin, a naturally occurring common dietary flavonoid, is mainly found in vegetables, fruits and other plants. It can regulate cellular signaling pathways related to disease progression. Quercetin is known to have a plethora of activities, ranging from anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, among others. But its medicinal potential is hindered because of it low bioavailability and limited selectivity due to poor water solubility and permeability. This study aims at synthesizing semi-synthetic derivatives of quercetin with a view to improve its bioavailability.
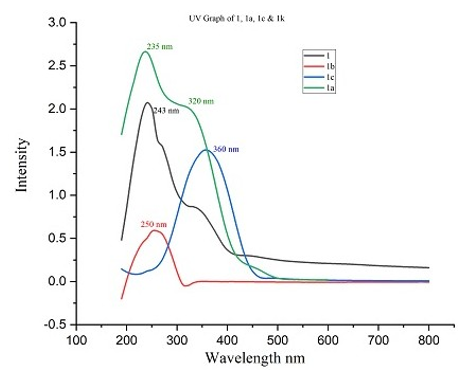
Fig. 1: Comparative UV plot of 1, 1a, 1b andn1c
Pages: 83-86 | 661 Views 39 Downloads
How to cite this article:
Chaitra S Shriyan, Iravati J Chengalur and Vishal Banewar. Advances in semi-synthetic derivatives of quercetin: Enhanced methodologies and pharmacological potential. J Pharmacogn Phytochem
2025;14(5):83-86. DOI: 10.22271/phyto.2025.v14.i5b.15554
Related Journal Subscription
Important Links
Important Sites
Copyright © 2012 - 2025. All Rights Reserved.







