- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 5 (2025)
Hepatoprotective effect of Sida cordifolia on tartrazine-induced toxicity in albino rats
Prakirnika Mishra and Veena B Kushwaha
This study evaluates the hepatoprotective effects of aqueous (AESC) and ethanolic (EESC) extracts of Sida cordifolia against tartrazine-induced hepato-toxicity in albino rats. Tartrazine, a widely used synthetic food dye, is known to cause oxidative stress and hepatocellular damage. Rats exposed to tartrazine exhibited significant decrease in levels of liver glycogen, protein, amino acids, DNA, RNA and activity of acid phosphatase along with an increase in activity of alkaline phosphatase, indicating liver dysfunction. Treatment with both aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Sida cordifolia significantly mitigated these biochemical alterations and restored hepatic function. The findings suggest that the extracts of Sida cordifolia, confers a protective effect against tartrazine-induced hepatotoxicity, probably through its antioxidant and membrane-stabilizing properties, highlighting its potential as a natural therapeutic agent.
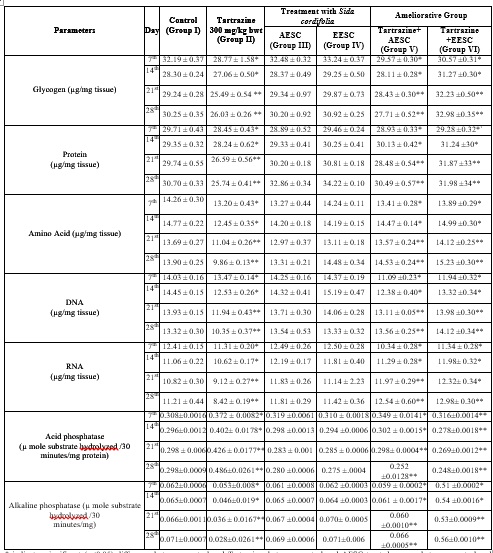
Fig. 1: The effects of oral administration of tartrazine, AESC and EESC, tartrazine + AESC, tartrazine + EESC on liver biochemical parameters in albino rats
Pages: 87-91 | 829 Views 49 Downloads







