- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 5 (2025)
Modulation of radiation-induced biochemical alterations in mice by Tylophora indica leaf extract
Sunil Kumar Meena, Ronit Parashar, Priyadarshi Meena and Dev Dutt Patel
Whole-body γ-irradiation (10 Gy) in mice induced marked oxidative stress in jejunal tissue, as evidenced by suppression of key antioxidants and enhanced lipid peroxidation. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities were significantly reduced following radiation exposure, while malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, indicative of lipid peroxidation, showed a marked increase. Oral pre-treatment with Tylophora indica hydro-methanolic leaf extract (TE, 100 mg/kg b.wt.) for seven days prior to irradiation provided notable radioprotection. TE supplementation enhanced SOD activity by up to 23% on day 1 and improved CAT levels by ~67% at day 3 compared to irradiated controls. Similarly, reduced glutathione (GSH) content was preserved, showing a 39% higher level across days 1-15, while lipid peroxidation was reduced by ~58% over the same period. Furthermore, TE pre-treatment significantly prevented protein loss in intestinal tissues, with pronounced recovery observed on day 15 post-irradiation. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that Tylophora indica hydro-methanolic leaf extract mitigates γ-radiation-induced oxidative stress by reinforcing endogenous antioxidant defenses, reducing membrane lipid damage, and preserving protein integrity.
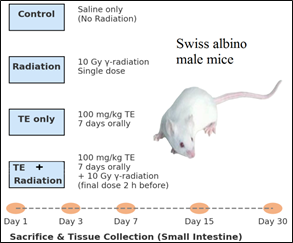
Fig. 1: Development of an experimental plan to investigate biochemical parameters.Development of an experimental plan to investigate biochemical parameters.
Pages: 258-266 | 223 Views 15 Downloads







