- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 5 (2025)
Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of essential oils from Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J. Presl (Lauraceae) and Allanblackia parviflora A. Chev (Clusiaceae)
N’DRI Koffi Alfred, Kouame Bosson Antoine, Monyn Epse Kouame Ebalah Delphine, Kouassi Kouamé Séraphin, Mamyrbékova-Békro Janat Akhanovna and Bekro Yves-Alain
The yield, chemical composition and antioxidant activity of Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J. Presl and Allanblackia parviflora A. Chev essential oils were determined after steam extraction. The yield of Cinnamomum camphora essential oil was 0.33±0.02%, compared with 0.01±0% for Allanblackia parviflora oil. These essential oils were analyzed by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Cinnamomum camphora oil is mainly made up of hydrocarbon monoterpenes (21.65%), oxygenated monoterpenes (73.92%), hydrocarbon sesquiterpenes (3.85%), oxygenated sesquiterpenes (0.27%) and other compounds (0.22%). The main compounds identified are: camphor (57.02%), eucalyptol (15.28%), α-pinene (7.45%) and β-pinene (4.01%). Allanblackia parviflora essential oil is made up of oxygenated monoterpenes (0.17%), hydrocarbon sesquiterpenes (80.05%), oxygenated sesquiterpenes (17.27%) and other compounds (2.32%). The dominant compounds are: α-caryophyllene (46.70%), caryophyllene (14.50%), humulene-1,2-epoxide (9.39%), β-selinene (8.72%). Evaluation of antioxidant activity revealed that the essential oils of Cinnamomum camphora (CR50=0.038±0.01 mg/mL; vit C: CR50=0.016±0.0089 mg/mL) and Allanblackia parviflora (CR50=0.043±0.01 mg/mL; vit C: CR50=0.016±0.0089 mg/mL) exhibited good antioxidant activity.
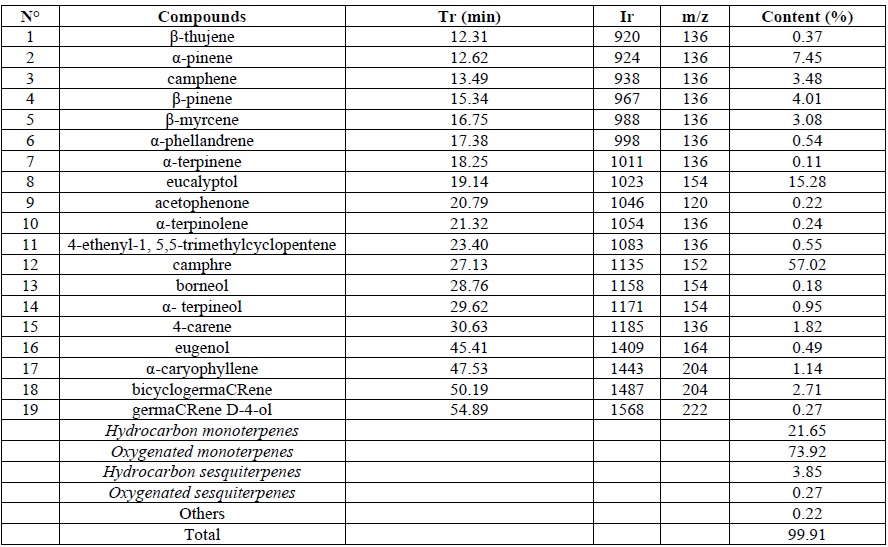
Fig. 1: Chemical composition of Cinnamomum camphora essential oil obtained by steam distillation
Pages: 657-661 | 247 Views 123 Downloads









