- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 6 (2025)
Comparative analysis of Aloe vera gel, epidermis, and whole leaf extracts for antimicrobial activity
Mark Fallah
The study examines the antimicrobial potential of ethanolic extracts from Aloe vera gel, epidermis, and whole leaf, using Thin Layer Chromatography. Aloe vera, a plant with medicinal and cosmetic properties, is gaining popularity due to its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and wound healing properties. Its natural health benefits are particularly important in the context of antibiotic infections. The study extracted Aloe vera gel, epidermis, and leaf from 90% ethanol and air-dried for analysis. The extracts were screened for alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, and terpenoids, and tested for antimicrobial activity. The gel extract showed no significant inhibition zones against all organisms, while the epidermis extract was most effective against Escherichia coli. This supports the therapeutic potential of Aloe vera epidermis as a natural antimicrobial agent. Further research is needed to determine Aloe vera's antimicrobial properties as a single active component, isolate and purify it, evaluate its activity in live creatures, and compare dried extracts.
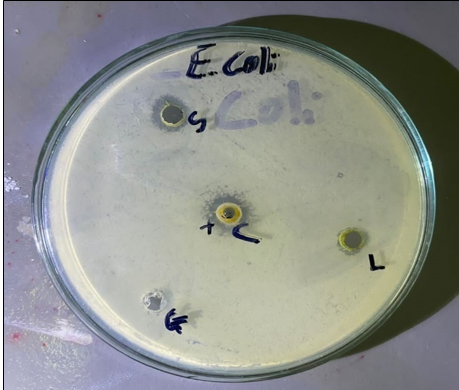
Fig. 1: Antimicrobial activity of different Aloe vera extracts on Escherichia coli 2.
Pages: 20-29 | 373 Views 216 Downloads









