- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 6 (2025)
Shooting an arrow against inflammasome: Novel plant phenolic derivatives as phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor
Amit Kumar and Jitendra Kumar Malik
Background: Inflammation refers to the body's typical physiological reaction to tissue injury. Such injuries can result from physical or mechanical harm, trauma, autoimmune responses, microbial infections, or burns. Inflammation can be categorized as either acute or chronic. PDE-4 is a key player in inflammation, as it regulates the levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) within inflammatory cells. This regulation is vital for the immune system's proper functioning and the resolution of inflammation. Phenolic compounds exhibit remarkable pharmacological and nutritional benefits, including antimicrobial, antibacterial, antiviral, anti-sclerosis, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects, which have garnered increasing interest from the scientific community.
Aim: This study seeks to examine the effectiveness of plant phenolic like chlorogenic acid, rutin, quercetin and gallic acid against PDE-4 to clarify their anti-inflammatory potential.
Method: PDE-4 was chosen as the target proteins in the current investigation. The bond was found using the Auto Dock software using a grid-based docking method. Compounds' 2D structures were generated, converted to 3D, and subsequently energetically lowered up to an arms gradient of 0.01 using the Merck Molecular Force Field (MMFF).
Results: The binding energy was found to be -4.06, -5.74, -6.76 & -3.55 kcalmol-1 for chlorogenic acid, rutin, quercetin & gallic acid respectively against PDE4 enzyme.
Conclusion: The finding of the in-silico molecular docking showed that selected lead compound is effective binds & inhibitory action on target protein.
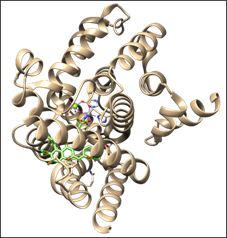
Fig. 1: Crystal structure of PDE4 enzyme with bound ligand 0X8(PDB ID-7F2K)
Pages: 270-277 | 37 Views 13 Downloads









