- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 15, Issue 1 (2026)
Phytochemical analysis and acute toxicity of Colocasia esculenta leaves for use in livestock
Djinandji Gnamien Marie-Claire, Zougrou N’guessan Ernest and Coffi Grace Melaine Manuela
The aim of this study is to promote African pharmacopoeia by analyzing the chemical composition and acute toxicity of the aqueous extract of Colocasia esculenta leaves, a plant commonly used in food and traditional medicine. The extract was prepared by macerating the leaves in distilled water and filtering the solution. It was then subjected to qualitative phytochemical screening and acute toxicity testing. Acute toxicity was evaluated in Wistar rats after a single oral administration of 2000 mg/kg body weight, following OECD Guideline 423, with body weight monitored throughout the experiment. Phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of sterols, polyterpenes, polyphenols, catechin tannins, flavonoids, alkaloids, and quinones, while saponosides were absent. The toxicity study showed no signs of toxicity at the tested dose. A slight increase in body weight was observed in treated rats compared to controls, indicating that Colocasia esculenta leaves are rich in bioactive compounds and safe for use.
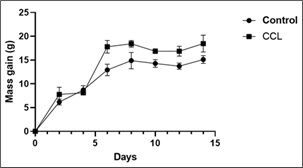
Fig. 1: Change in body weight of rats after administration of a single dose of 2000 mg/kg body weight of aqueous extract of Colocasia esculenta leaves
Pages: 302-305 | 27 Views 8 Downloads









