- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 15, Issue 1 (2026)
Formulation and evaluation of anti-pigmentation bio-ferment cream for cosmetic skincare applications
Shami Ahmad, Md Hasheem Khan, Ijlal Husain, Aamir Imam and Sagufta Farheen
The rising demand for safe, effective, and natural skincare solutions has led to a surge in herbal-based cosmetic formulations. This study presents the development and evaluation of a novel anti-pigmentation cream utilizing herbal bioferments. A cutting-edge approach that enhances the efficacy of traditional plant extracts through microbial fermentation. Unlike conventional creams that rely on raw herbal extracts, this formulation incorporates fermented liquorice, turmeric, rice water, and green tea, each selected for their proven depigmenting, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Fermentation, carried out using Lactobacillus plantarum or Saccharomyces cerevisiae, transforms these botanicals into smaller, bioavailable molecules, improving skin penetration and reducing irritation. The cream is formulated through a standard emulsification process, combining an oil phase (shea butter, almond oil, glyceryl monostearate, cetyl alcohol) with an aqueous phase (purified water, glycerin, aloe vera juice), followed by the incorporation of active bioferments and supportive additives like panthenol, vitamin E, and Geogard ECT preservative. Evaluation parameters include organoleptic properties, pH, stability, spreadability and irritancy under various conditions.
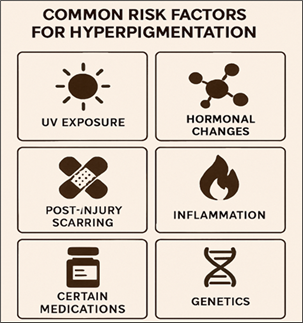
Fig. 1: Common risk factors for hyperpigmentation
Pages: 308-317 | 39 Views 12 Downloads









