- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal

Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry
Vol. 14, Issue 5 (2025)
Comparative Phytochemical and Physicochemical Study of Chitrak (Plumbago zeylanica Linn.) as Abhāva-pratinidhi Dravya for Bhallātaka (Semecarpus anacardium Linn.)
Amol Krushna Pable and Aparna Ghotankar
In Ayurvedic pharmaceutics, the principle of Abhāva-pratinidhi dravya (substitute drug in absence of the original) plays a crucial role in ensuring continuous therapeutic availability without compromising efficacy. Bhallātaka (Semecarpus anacardium Linn.) is widely used in classical formulations for its Kaphahara, Vātahara, Lekhana, and Deepana properties. However, due to issues of scarcity, seasonal availability, allergenic potential, and strict processing requirements, substitution with a pharmacologically and phytochemically similar drug is justified. Chitrak (Plumbago zeylanica Linn.) has been mentioned in Ayurvedic classics as a possible substitute due to its Deepana, Pachana, and Lekhana actions. This article presents a comparative analysis of the phytochemical profile and physicochemical parameters of both drugs to establish Chitrak as a potential Abhāva-pratinidhi dravya for Bhallātaka.
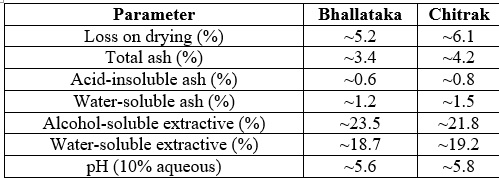
Fig. 1: Physicochemical Parameters
Pages: 25-27 | 1315 Views 44 Downloads







